

What is the frequency of big R, little r now a common thing is for kids to go "0.16 can't roll their tongues" that's q no. 16% of the population cannot roll their tongues. Now an example kind of a problem that you're going to face when you're studying Hard-Weinberg is one like this, for example in a population 0.16 of that population i.e. q squared is the frequency of little r, little r or homozygous recessive individuals and again this is for a population that's in something called genetic equilibrium that's where there's no changes going on from one generation to the next in terms if these frequencies either of the genotypes or frequencies of the alleles within the gene pool. In my example of tongue rolling it's big R, big R, 2pq is the frequency of big R, little r or heterozygous individuals. What's p squared? p squared is the frequency of individual who has homozygous dominant.

#HARDY WEINBERG EQUATION CALCULATOR PLUS#
So I get p squared plus 2pq plus q squared equals 1. What I did is I took my p+q=1 and I just did what you've done before in your Math classes I squared both sides you know in Math if you do one thing to one side of the equation, you can do it to the other side of the equation and things still work out. Now it gets a little bit more complicated when we go to the equation for describing the individual population's genotypes, but don't worry because you've actually seen this before. And I could say well if p is 0.625 then I know 1-0.625 is 0.375 alright that's pretty straight forward. One I can still go 1, 2, 3 divide by 8 or I could pop into my Hardy-Weinberg equation here p+q=1 and do some subtraction. What is p and whit is q in my gene pool? Well I would solve this simply by counting up 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 big R alleles out of the total number in my gene pool of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 alleles which gives me 0.625 so p in this case is 0.625 whereas q is I could solve this in 2 ways. Alright so if our population consisted of somebody's homozygous dominant, another persons who is homozygous dominant, somebody who is heterozygous for the tongue rolling ability and then somebody who is homozygous recessive. Q is the frequency of the recessive allele within that gene pool, little r in this case or the inability to roll your tongue. And then you need to understand that gene pool is this abstract idea, it's the collective, or a collection of all the alleles within a particular population for any trade that you're talking about.įor example let's suppose that we had this population here now the Hardy-Weinberg equation for describing that gene pool is p+q=1, now p is a variable used to represent the frequency of the dominant allele in this case I'll be talking about the trait big R for rolling your tongue. So I need to make sure that you understand some basic ideas first population is a group of organisms within a particular area where all are in a breeding with each other.
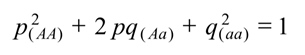
The Hardy-Weinberg Law is a collection of two equations that is used to Mathematically calculate the frequencies of alleles within the gene pool of a population and the frequency of genotypes within that population. One of the basic things in population genetics is a concept known as the Hardy-Weinberg Law.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
